Implementation of Hash Map in Python

1. Definition:
A hash table is a data structure that provides a mapping from keys to a values using techique called “hash”.
2. Hash Function:
A Hash function H(x) is a function that maps a key “x” to a hash table index in a fixed range.
3. Properties of Hash Function
- If H(x) = H(y) then value of x and y might be equals, but if H(x) != H(y) then value of x and y are certainly not equal.
- A hash function H(x) must be deterministic. This means that if H(x) = y then H(x) must always produce y and never produce other value.
- We will try very hard to make uniform hash function(ideally) to minimize the number of hash collision.
4. Hashable
Since we are going to use hash functions in the implementation of our hash table, we need our hash functions to be deterministic. To enforce this behavior we demand that the keys used in our hash table to be immutable data types. Hence, if a key of type-T is immutable, and we have a hash function H(k) defined for all keys k of type-T then we say a key of type-T is hashable.
In Python, mutable type such as “list”, “set”, “dict” etc.. are not hashable.
5. How a Hash Table Work?
Ideally we would like to have a very fast insertion, lookup and removal time for the data. we are placing in our hash table. Remarkably, we can achieve all this in O(1) time using a hash function as a way to index into hash tables.
The constant time behavior attributed to hash tables is only true if you have a good uniform hash function
6. What is Collision and How to Handle?
A hash collision is when two key x, y hash to the same value which is H(x) = H(y)
There are 2 primary ways to handle this situation:
1. Separate chaining:
This approach deals with hash collisions by maintaining a data structure (usaually a linked list) to hold all the different values which hashed to a particular value.
2. Open Addressing:
This approach deals with hash collisions by finding another place within the hash table for the k-v to go by offsetting(by probing function P(x)) it from the position to which it hashed to.
7. Chaos with cycles
If we implement hash table with open addressing and collision occurs, we have to use the probing function to get the next position to store the value. There might be a issue of causing cycle. (there are still available position in hash table, but probing can’t reach due to the cycle).
To solve this problem we can do it by properly set the size and probing factor in different kind of probing strategies.
Rules:
1. linear - ax + b –> let a = 1 or gcd(a, size) = 1
2. quadratic - ax^2 + bx + c –> choose (x^2 + x) / 2 and size is a power of 2
3. double hashing - p(x, k) = x * h’(x) –> linear hashing –> gcd(h’(x), size) must be 1 –> choose size to be prime.
8. Max Load Factor
A hash table has to adjust the size as the data stored increases. A max load factor is a flag to indicated whether the table size should increase. A proper used of max load factor can prevent the worst case complexity occurs.
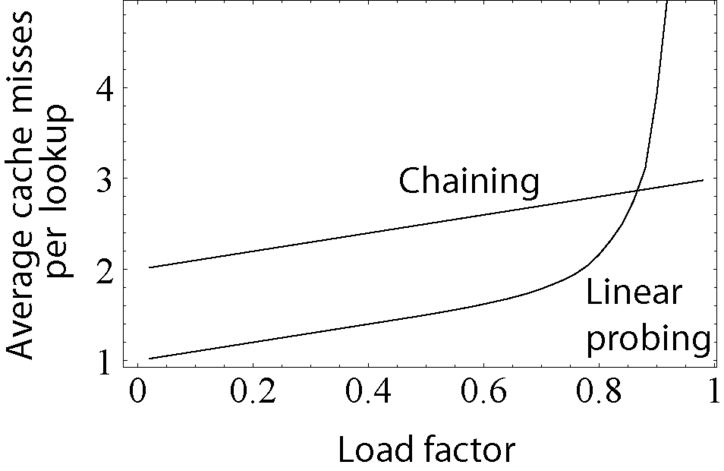
9. Complexity
| Operation | Average | Worst |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion | O(1) | O(N) |
| Removal | O(1) | O(N) |
| Search | O(1) | O(N) |
In the worst case which every key is hashed to the same hash idx, hash table depreciates to a linear structure such as array or linked list.
10. Implementation
- Separate Chaining Hash Table:
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, x):
self.key = key
self.data = x
self.next = None
class HashWithSeparateChaining:
def __init__(self, size):
if size <= 0:
raise Exception('size must greater than 0')
self.hash_table = [None for _ in range(size)]
self.count = 0
self.size = size
self.max_load_factor = 0.4
def _get_threshold(self):
return int(self.size * self.max_load_factor)
def __repr__(self):
ret = ''
for idx, e in enumerate(self.hash_table):
line = 'idx: {}, chaining: '.format(idx)
chaining = []
while e is not None:
chaining.append('(key:{}, value:{})'.format(e.key, e.data))
e = e.next
ret += line + '->'.join(chaining) + '\n'
return ret
def _hash_func(self, key):
return key % self.size
def _expand_and_reallocate(self):
self.size = self.size * 2
pre_hash_table = self.hash_table
self.hash_table = [None for _ in range(self.size)]
for e in pre_hash_table:
while e is not None:
self.insert(e.key, e.data, is_relocated=True)
e = e.next
def insert(self, key, value, is_relocated=False):
hash_idx = self._hash_func(key)
idx_head = self.hash_table[hash_idx]
if idx_head is None:
self.hash_table[hash_idx] = Node(key, value)
else:
while idx_head.next is not None:
if idx_head.key == key and idx_head.data == value:
return
idx_head = idx.next
idx_head.next = Node(key, value)
self.count += 1
if self.count > self._get_threshold() and not is_relocated:
self._expand_and_reallocate()
def search(self, key):
hash_idx = self._hash_func(key)
idx_head = self.hash_table[hash_idx]
while idx_head is not None:
if idx_head.key == key:
return idx_head.data
idx_head = idx_head.next
raise Exception('key not in found')
def remove(self, key):
hash_idx = self._hash_func(key)
idx_head, pre = self.hash_table[hash_idx], None
while idx_head is not None:
if idx_head.key == key:
if pre is None:
self.hash_table[hash_idx] = idx_head.next
else:
pre.next = idx_head.next
self.count -= 1
return
pre = idx_head
idx_head = idx_head.next
raise Exception('key not in found')
- Open Addressing Hash Table:
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, x):
self.key = key
self.data = x
class DeadNode:
pass
class OpenAddressingHashTable:
def __init__(self, size=10):
if size <= 1:
raise Exception('hash table size less than 1')
self.hash_table = [None for _ in range(size)]
self.size = size
self.total_count = 0
self.max_load_factor = 0.4
def __repr__(self):
ret = ''
for idx, e in enumerate(self.hash_table):
line = 'idx: {}, '.format(idx)
if e is not None:
if e is DeadNode:
line += 'Deadnode'
else:
line += 'key: {}, val: {}'.format(e.key, e.data)
else:
line += 'None'
ret += line + '\n'
return ret
def _get_threshold(self):
return int(self.size * self.max_load_factor)
def _hash_func(self, key):
return key % self.size
def _probing_func(self, hash_idx, count):
offset = count + 0
return (hash_idx + offset) % self.size
def _expand_and_reallocate(self):
self.size = self.size * 2
pre_hash_table = self.hash_table
self.hash_table = [None for _ in range(self.size)]
for e in hash:
if e is not None:
self.insert(e.key, e.data)
def _insert(self, idx, node):
self.hash_table[idx] = node
self.total_count += 1
if self.total_count > self._get_threshold():
self._expand_and_reallocate()
return
def insert(self, key, value):
hash_idx = self._hash_func(key)
idx = hash_idx
prob_term = 1
idx_set = set()
while 1:
idx_set.add(idx)
node = self.hash_table[idx]
if node is None or node is DeadNode:
self._insert(idx, Node(key, value))
return
elif node.key == key:
return
idx = self._probing_func(hash_idx, prob_term)
prob_term += 1
if idx in idx_set: # chaos of cycles
if len(prob_idx_set) == self.size:
self._expand_and_reallocate()
self.insert(key, value)
break
else:
raise Exception('hash table issue: chaos of cycles')
def search(self, key, to_return_idx=False):
hash_idx = self._hash_func(key)
idx = hash_idx
prob_term = 1
idx_set = set()
while 1:
idx_set.add(idx)
node = self.hash_table[idx]
if node is None:
raise Exception('key not found')
elif node is not DeadNode:
if node.key == key:
return node.data if not to_return_idx else idx
idx = self._probing_func(hash_idx, prob_term)
prob_term += 1
if idx in idx_set:
if len(idx_set) == self.size:
raise Exception('key not found')
else:
raise Exception('hash table issue: chaos of cycles')
def remove(self, key):
idx = self.search(key, to_return_idx=True)
self.hash_table[idx] = DeadNode